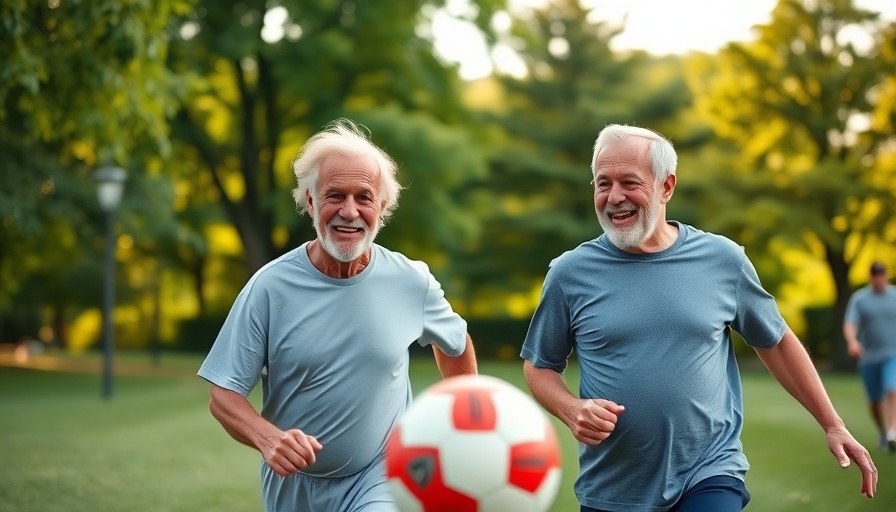

Football Training: A New Path in Cardiac Rehab
In an inspiring breakthrough, a structured football training program is showing significant benefits for patients grappling with heart-related health issues. Research from Germany has shown that engaging in a 75-minute weekly football training session over the course of a year can result in impressive health improvements for individuals aged 40 and above who have experienced a myocardial infarction (MI) or suffer from coronary artery disease (CAD). This innovative approach not only increases physical fitness but plays a pivotal role in secondary prevention strategies.
Key Findings from the Study
The study, conducted on 89 participants who engaged in weekly football training compared to a control group of 88 individuals following standard prevention recommendations, showcased remarkable outcomes. The trial recorded a significant rise in maximum oxygen uptake in the football group from 18.0 to 19.7 mL/min/kg, revealing enhanced cardiovascular fitness (P < .001). In contrast, the control group saw a decrease from 19.5 to 18.3 mL/min/kg (P = .046).
Moreover, blood pressure levels in football participants showed a decrease from 132/81 mm Hg to 125/76 mm Hg, highlighting an effective reduction in a critical cardiovascular risk factor (P < .001). In sharp contrast, the control group exhibited no significant change, often requiring more antihypertensive medications, thus underscoring the advantage of an active lifestyle enriched by team sports like football.
The Mental Health Benefits
Beyond physical health improvements, football training helped address mental health concerns. Participants in the football group reported better weight management and significant improvements in depressive symptoms (P < .05), which points to the holistic advantage of incorporating physical conditioning through sports into cardiac rehab programs. For many patients, engaging in football not only fosters physical fitness but also offers social interaction and emotional support, which are crucial for overall well-being.
A Future for Football in Cardiac Care
As echoed by the study's author, Bastian Schrader from the University of Oldenburg, football presents an accessible option for enhancing patient care in cardiovascular rehabilitation. The existing infrastructure for organized football activities across communities provides a cost-effective and enjoyable outlet for physical activity—essentially making it a viable part of health intervention programs.
The Broader Implications
The implications of these findings go beyond just cardiac rehabilitation. They serve as a reminder of the importance of structured physical activity in preventative care. More studies could shed light on how team sports and specific training programs could be tailored to meet the needs of different populations at risk for heart diseases, thereby promoting a more active and healthier lifestyle.
Conclusion: The Power of Team Sports
This study transforms the narrative around traditional cardiac care and invites medical practitioners and health policymakers to consider how integrating enjoyable, community-based activities like football could radically enhance patient outcomes. The pathway laid out here indicates that investing in physical wellness through sports not only aids patients in managing their heart conditions but also fosters a supportive community environment.
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 


 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 

Write A Comment